MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
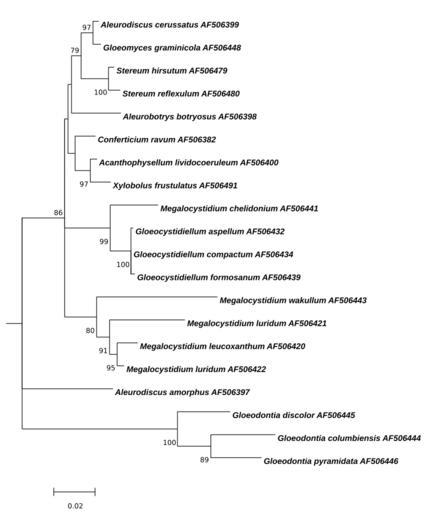
| View Original: | Megalocystidium-Mamximum-Likelihood-Tree.svg (112x134) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
| Keywords: Megalocystidium-Mamximum-Likelihood-Tree.svg Megalocystidium Figure Molecular Phylogenetic analysis of Megalocystidium by the Maximum Likelihood method<br/> The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Kimura 2-parameter model 1 The tree with the highest log likelihood -4055 6447 is shown The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches A user-specified tree was used as an initial tree in the heuristic search A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites 5 categories +G parameter 1 0022 The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable +I 71 5627 sites The tree is drawn to scale with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site The analysis involved 20 nucleotide sequences All positions with less than 95 site coverage were eliminated That is fewer than 5 alignment gaps missing data and ambiguous bases were allowed at any position There were a total of 1158 positions in the final dataset Evolutionary analyses were conducted in http //megasoftware net/ MEGA6 2<br/> 1 Kimura M 1980 A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences Journal of Molecular Evolution 16 111-120 <br/> 2 Tamura K Stecher G Peterson D Filipski A and Kumar S 2013 MEGA6 Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6 0 Molecular Biology and Evolution30 2725-2729 <br/> http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506400 Acanthophysellum lividocoeruleum AF506400 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506398 Aleurobotrys botryosus AF506398 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506399 Aleurodiscus cerussatus AF506399 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506382 Conferticium ravum AF506382 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506432 Gloeocystidiellum aspellum AF506432 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506434 Gloeocystidiellum compactum AF506434 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506439 Gloeocystidiellum formosanum AF506439 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506444 Gloeodontia columbiensis AF506444 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506445 Gloeodontia discolor AF506445 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506446 Gloeodontia pyramidata AF506446 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506448 Gloeomyces graminicola AF506448 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506441 Megalocystidium chelidonium AF506441 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506420 Megalocystidium leucoxanthum AF506420 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506421 Megalocystidium luridum AF506421 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506422 Megalocystidium luridum AF506422 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506443 Megalocystidium wakullum AF506443 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506479 Stereum hirsutum AF506479 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506480 Stereum reflexulum AF506480 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506491 Xylobolus frustulatus AF506491 http //www ncbi nlm nih gov/nuccore/AF506397 Aleurodiscus amorphus AF506397 own 2014-09-09 Thkgk Cc-zero other versions Megalocystidium | ||||